A Beginner’s Guide to Compounding Interest
Compounding interest is a powerful financial tool that can help individuals build wealth over time. According to Investopedia, it is defined as “interest on a loan or deposit added to the previous balance, which in turn increases the interest paid in the following period.”
This concept is crucial for anyone looking to secure their financial future. By understanding how compounding interest works, individuals can make informed decisions about their investments and savings, potentially leading to significant long-term gains.
As a fundamental concept in financial planning, compounding interest has the potential to greatly impact one’s financial stability and growth.
Understanding the Power of Compounding Interest
The power of compounding interest lies in its ability to generate interest on interest, making it a potent financial tool for growing your savings or investments over time.
Compounding interest works by adding interest to the principal amount, creating a new, higher principal for the next interest calculation. This process can lead to substantial financial growth, as the interest earned in previous periods becomes the base for the next period’s interest calculation.
As a result, understanding compounding interest is crucial for making informed decisions about your financial resources. By harnessing the power of compounding, you can potentially achieve your long-term financial goals more efficiently.
Financial growth through compounding interest is not limited to large investments; even modest savings can benefit from this powerful financial concept.
The Mathematics Behind Compounding Interest
To grasp the true potential of compounding interest, it’s essential to understand the underlying mathematics. The formula for compound interest is given by [P (1 + i)n] – P, where P is the principal amount, i is the annual interest rate, and n is the number of compounding periods.
Breaking down the formula reveals the importance of each component. The principal amount (P) is the initial investment. The annual interest rate (i) determines the rate at which interest is earned. The number of compounding periods (n) affects how frequently interest is compounded, significantly impacting the total amount.
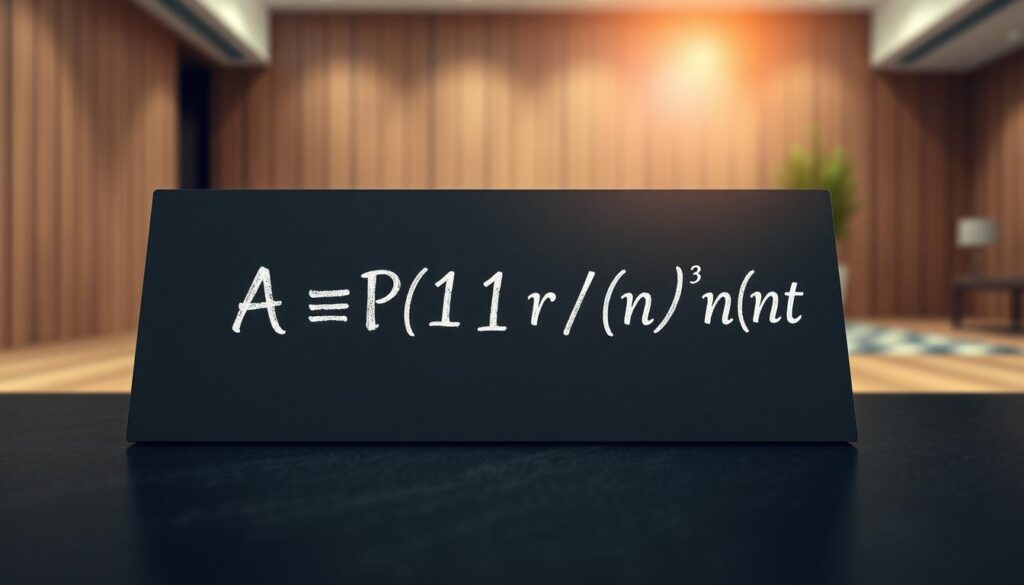
Understanding these elements and how they interact is crucial for financial calculations. By applying the compound interest formula, individuals can predict their investment growth over time, making informed decisions about their financial strategies.
A Beginner’s Guide to Compounding Interest: Real-World Examples
Real-world examples provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of compounding interest in achieving long-term financial goals. By examining different scenarios, we can better understand how compounding interest can lead to significant financial gains over time.
For instance, saving $100 a month at age 20 can lead to a substantial retirement fund by age 65, thanks to the power of compounding. This early start allows the interest to compound over a longer period, resulting in a larger sum. In contrast, starting to save the same amount at age 40 will yield a significantly lower total amount by age 65, highlighting the importance of early financial planning.

Another example is investing in a high-yield savings account or certificate of deposit (CD) that offers compound interest. These financial instruments can help grow your savings over time, providing a nest egg for future expenses or emergencies. By understanding how compounding interest works, individuals can make informed decisions about their financial planning and choose the best options for their needs.
In conclusion, real-world examples demonstrate the potential of compounding interest to enhance financial well-being. By starting early and making informed investment choices, individuals can harness the power of compounding to achieve their long-term financial goals.
The Rule of 72: A Simple Way to Estimate Growth
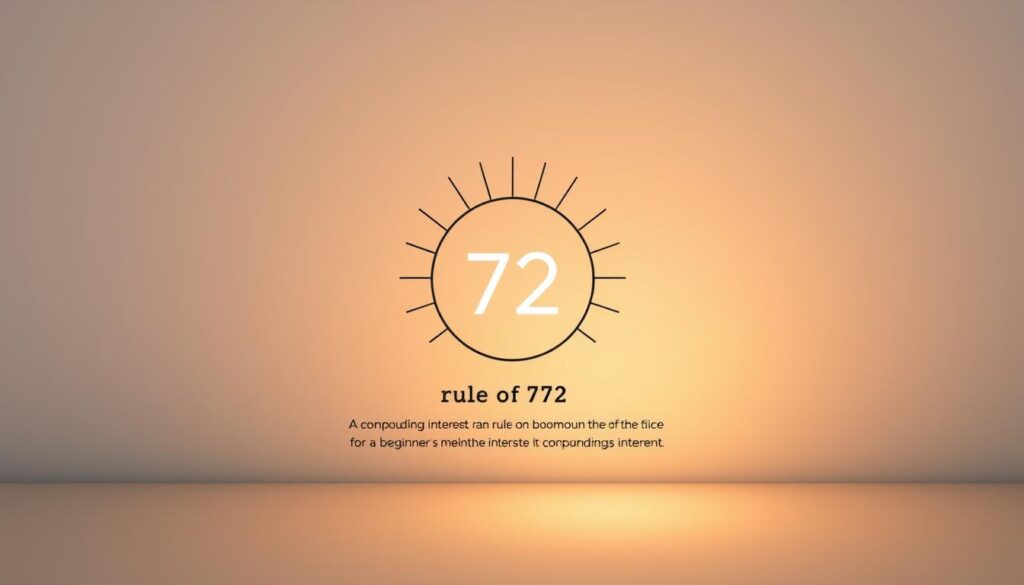
The Rule of 72 is a handy formula that provides a quick estimate of how long it will take for an investment to double in value. It is calculated by dividing 72 by the annual interest rate.
For example, if you have an investment that earns an annual interest rate of 6%, you can estimate that it will take approximately 12 years for your investment to double (72 / 6 = 12). This rule provides a straightforward way to compare different investment opportunities and understand their potential for growth.
The Rule of 72 is particularly useful for financial planning, as it gives investors a simple tool to estimate the impact of different interest rates on their investments. However, it’s worth noting that this rule is most accurate for interest rates between 5% and 10%. For rates outside this range, the estimate may be less accurate.
Leveraging Compounding Interest for Wealth Building
Effective wealth building through compounding interest starts with leveraging the power of automated reinvestment options. By doing so, individuals can maximize their returns and achieve their financial goals more efficiently.
Automated reinvestment options allow investors to take advantage of compounding interest without having to manually reinvest their earnings. This can be particularly beneficial for those who want to grow their wealth over time without constant intervention.
Automated Reinvestment Options
One popular automated reinvestment option is the dividend reinvestment plan (DRIP) offered by many brokerage accounts. An investor opting for a DRIP is essentially using the power of compounding in their investments. By reinvesting dividends, investors can purchase additional shares, thereby increasing their potential for future earnings.
To further leverage compounding interest, individuals can also consider setting up automatic transfers from their checking accounts to their investment or savings accounts. This way, they can ensure consistent growth of their investments over time.
By combining automated reinvestment options with a solid understanding of compounding interest, individuals can create a powerful wealth-building strategy that helps them achieve their long-term financial goals.
Tools and Resources to Track Your Compounding Growth
To effectively track your compounding growth, it’s essential to utilize the right financial tools and resources. Various online calculators and spreadsheet software are available to help individuals monitor their compounding interest.
One of the most popular tools is the online compounding interest calculator, which allows you to input your initial investment, interest rate, and time period to calculate your returns.
Additionally, spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets can be used to create custom spreadsheets to track your investments and returns. These tools provide a clear picture of your financial growth and help you make informed decisions.
By leveraging these resources, you can optimize your financial planning and achieve your long-term goals.
Conclusion
Understanding compounding interest is a crucial aspect of financial planning. As discussed in A Beginner’s Guide to Compounding Interest, this powerful financial tool can help individuals achieve their long-term financial goals.
A compounding interest summary highlights the importance of starting early and being consistent. By leveraging high-yield savings accounts, individuals can maximize their savings potential. For instance, a $10,000 deposit in a high-yield savings account earning 2% annual interest could make around $200 in one year.
To make the most of compounding interest, it’s essential to track your growth and adjust your strategy as needed. By doing so, you can ensure you’re on track to meet your financial objectives. With the right tools and resources, you can create a personalized financial plan that suits your needs.
By applying the concepts learned in A Beginner’s Guide to Compounding Interest, you can take control of your financial future and make informed decisions about your savings.






